Histamine Intolerance Syndrome
There are not many issues that can cause so many problems in virtually every area of the body than Histamine Intolerance (HIT). The following is from a lecture I gave the doctors at the Biologix Center. Although every doctor has been extensively trained at the post-graduate level in virtually every pathology known to mankind, as you will see here, HIT is a specialty of its own, since there is so much to know. The following are just the bullet points outlining everything you would want to know about HIT.
Histamine Intolerance has been called a “Pseudo-Allergy,” because many of its symptoms appear to be allergies when in fact they are not truly IgE-mediated, Type-1 hypersensitivity reactions typically seen in those suffering with allergies.
It is likely that some level of histamine intolerance is aggravating the condition of any person suffering from the many chronic, degenerative or inflammatory illnesses. Without our BRS testing to help guide our doctors, it would be a very difficult quagmire to navigate a person to resolution. Thankfully we can often rapidly find and address many of the possible causes, though it is definitely a lengthy process to dig deep enough to figure out all the various things that have created this systemic issue and how to then facilitate the body’s restoration of how it handles histamine.
This article will also provide you with the information of things you need to avoid in your diet, as well as medications, and even natural supplements that might be promoting the overproduction of histamine.
Before you say, “This isn’t my problem” please read this article thoroughly and possibly print it out for your doctor so that they can possibly help you.
What is the difference between Allergies and Histamine Intolerance?
- Allergies are an IgE mediated, histamine response to an allergen, i.e., pollen or cat dander.
- Histamine Intolerance (HIT) is a toxic response by the body due to the excessive accumulation of endogenous or exogenous histamine from an inability of the body to efficiently breakdown histamine and hypersensitivity of cell antigen receptors.
Histamine Intolerance is caused by:
- The Over production of Histamine.
- The decreased ability of the body to breakdown histamine.
- Decreased Diamine Oxidase (DAO) enzyme production in the body.
- Histamine is broken down by oxidative deamination by DAO (former name: histaminase).
- Decreased Histamine N-Methyl Transferase (HNMT) enzyme production in the body which is needed to breakdown histamine.
- Histamine is broken down by ring methylation as a result of histamine-N-methyltransferase (HNMT).
See how many systems and symptoms can be caused by HIT
Symptoms of Histamine Intolerance (HIT)
- Histamine serves various functions in our body. This is why histaminosis may trigger a wide range of symptoms, affecting different organ systems.
- People suffering from HIT may display highly diverse symptoms. Every person has individual weak spots, which may be afflicted earlier than other parts in the body. Sufferers may be troubled by many of the following symptoms, either simultaneously or alternately.
- Some afflictions are chronic or very frequent, others may only occur sporadically. The symptoms are so varied that the people affected by HIT often do not suspect a single trigger.
HIT and Gastro-intestinal and Urinary Symptoms
- The most frequently observed troubles that occur with HIT are acute or chronic gastrointestinal symptoms.
- Irritable stomach or an irritable bowel respectively. A direct connection between food intake and the symptoms is often difficult to discern. This is due to the fact that the ingredients of ingested foods are only slowly absorbed by the body during the bowel transit time, which may last several hours, so that problems may only manifest themselves with a considerable delay.
- Eating aged or leftover foods, or those with high histamine content, may trigger abdominal cramps and severe diarrhea within 15-30 minutes.
- Digestive problems, flatulence, abdominal pain, stitch, stomach or intestinal cramps, frequent or chronic diarrhea, morning diarrhea.
- Histamine increases the motility of the bowel movements, so that the bolus passes the intestines faster than normal, which impairs the absorption of nutrients because of the short retention time.
- More rarely also constipation or constipation alternating with diarrhea.
- Heart burn, acid reflux (increases HCl).
- Inflammatory gastro-intestinal disorders, irritable bowel syndrome.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Frequent and/or painful, burning urination, interstitial cystitis.
- Symptoms similar to gastric flu (gastroenteritis).
HIT and Nervous System Symptoms
- Histamine plays a role in the regulation of the circadian rhythm and acts as neurotransmitter.Histamine stimulates the production of melatonin.
- High levels of histamine (as well as high melatonin) in the body may lead to a wide range of neurological symptoms. Neurological symptoms are in particular pronounced with a HNMT enzymopathy. Headache, fatigue, sleep disturbance may also be typical symptoms of a DAO enzymopathy.
- Headache, migraine, feeling of pressure in the head, dizziness.
- Fatigue, loss of energy, lack of motivation, exhaustion.
- Insomnia, problems falling asleep or sleeping through the night, only superficial catnapping without deep sleep, dreamlessness.
- Lack of concentration, impairment of cognitive performance, slowness.
- Tourette’s Syndrome.
- Noise sensitivity, search for tranquility and uneventfulness, vulnerability for sensory overload.
- Susceptibility to stress, impaired ability to withstand stress, feeling of burnout (feeling of mental and nervous exhaustion and breakdown).
- Clearing of throat in stress situations.
- Tension, nervousness, jumpiness (also without external cause), restlessness, tingling sensation, feeling of caffeine overdose.
- Muscle twitching, tremor, clenched jaws, grinding of teeth (bruxism), worn down teeth.
- Symptoms similar to those of poisoning with a mild neurotoxin.
- Melancholia, sadness, weepiness, depressive moods, depressions (often without visible cause).
- Thoughts of suicide.
- Temporary loss or impairment of the sense of smell.
- Personality changes, perhaps other mental/neurological disturbances.
- Drop in blood pressure, low blood pressure (hypotension)
- Cardiac arrhythmias
- Palpitation (stronger heart beat caused by a release of adrenaline)
- Racing heart (tachycardia), Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia (POTS)
HIT and Endocrine System
- Altered insulin sensitivity
- Dysmenorrhea (menstrual cramps)
- Amenorrhea
- Endometriosis
- Development disorder, failure to thrive
HIT and Immune System
- Increased susceptibility to infectious diseases, frequent infections.
- increased susceptibility for inflammations, inflamed areas.
- Sore throat
- Hoarseness
- Flulike symptoms without defined onset of disease, prolonged malaise, pain in the limbs.
- Sinus infection (sinusitis): frontal sinusitis, maxillary sinusitis, inflammation of other sinuses such as sphenoid or ethmoid sinuses.
- Constant swelling painful lymph nodes.
- Tonsillitis, adenoid vegetation (adenoid hyperplasia), possible surgical removal of tonsils. (The tonsils serve the immune defense. Their removal may further acerbate the increased susceptibility for infectious diseases.)
- Lump in one’s throat
- Autoimmune illness. Inflammation of connective tissue: tissue underneath the skin with inflammatory pain or tenderness.
- Painful feeling of inflammation, heat or pressure in the head, chronic (non-bacterial) inflammation of the brain (chronic encephalitis).
- Painful/burning bladder, desire to void, frequent urination (similar to bacterial bladder infection).
- Conjunctivitis, irritated reddened eyes, itching of the eyes.
- Yellow-white mucus secretions collect in the corners of the eyes.
- Misted, impaired vision
- Inflammatory rheumatic diseases, rheumatoid arthritis (e.g. knuckle joint rheumatism).
- Soft-tissue rheumatism: e.g. pain in the tendons or joints, back pain: the back muscles hurt similar to a strained muscle/muscle ache (muscular rheumatism, inflammation of a muscle).
- Periodic toothache, inflammation of the gums or wisdom teeth.
- Herpes simplex labialis (oral herpes, cold sores) or symptoms similar to herpes (e.g. badly healing skin cracks).
HIT and Skin
- Excessive sweating, attack of sweating, night-time sweating, perspiring hands/feet, hot flashes.
- Flushing of face following meals (flush), heat build-up, facial skin feels slightly irritated.
- Skin blemishes, acne, pimples, blackheads, overproduction of sebaceous gland, oily skin.
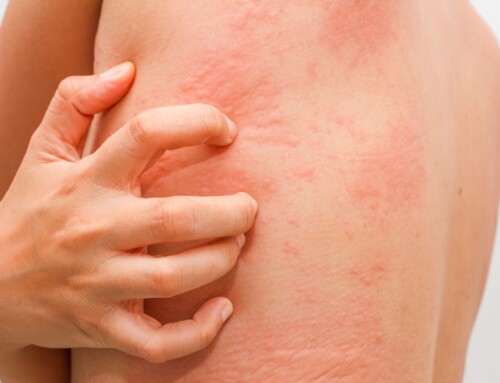
- Rashes, flushes, itching, eczema, hives (urticaria).
- Atopic eczema, Atopic dermatitis, Itching (e.g. itchy scalp, itchy vaccination scars).
- Physical irritation such as scratching, strokes or heat triggering flashes/rash or itching.
- Upper arms covered in little red spots/pimples, partially keratinised or purulent (impaired keratinisation), perhaps in connection with pollen allergies?• Hands with burning/aching inflammation/blisters/nodules/calluses.
- Sun allergy: the skin goes very quickly red in the sun, but the sunburn disappears on the following day.
- Dry lips
HIT and Respiratory Symptoms
- Bronchial Asthma
- Perennial rhinitis, swelling of nasal mucous membrane, runny nose (rhinitis, rhinorrhea) especially after food intake, also independent from type and histamine content of food, possibly aggravated by cold/smoke/smog/smells.
- Blowing the nose may lead to nosebleed (because of increased permeability of the blood vessels).
- Aphtha lesions of the oral mucosa, which become small yellow-white holes/wounds that hurt and will not heal for days and sometimes months. In addition to the oral mucosa, some papillae on the tongue may hurt like an aphtha.
- Chronic cough, constant tickly throat, dry cough, bronchitis, irritated bronchia.
- Constant clearing of the throat, particularly in stress situations.
- Sputum: viscid mucus to expectorate, frequent clearing of throat, perhaps also breathy vocal cords, particularly after sumptuous meals (similar to cystic fibrosis).
HIT and Fluid Regulation Symptoms
- Edema (Swelling because of fluid retention in the interstitial tissue).
- Swollen eyelids
- Leg swelling
- Abdominal bloating
Possible Miscellaneous HIT Symptoms
- Sensitivity to EMF pollution, WiFi, etc.
- Sensitive to Geopathic stressors
- Sensitive to Enviropathic stressors
DAO vs HNMT (The two pathways your body has to break down histamine)
- Diamine Oxidase enzyme (DAO) expression is restricted to specific tissues; the highest activities are shown for small intestines, ascending colon, and for placenta and kidney. DAO is responsible for scavenging extracellular histamine (i.e., after ingestion of histamine-rich food) after mediator release.
- Histamine N-Methyltransferase enzyme (HNMT) is widely expressed in human tissues; the greatest expression is in kidney and liver, followed by spleen, colon, prostate, ovary, spinal cord cells, bronchi, and trachea. HNMT is regarded as the key enzyme for histamine degradation in the bronchial epithelium. HNMT can convert histamine only in the intracellular space of cells.
Sources of Histamine and the cellular release of Histamine
- Foods containing histamine
- Mast cell dysregulation releasing excessive histamine
- Mental/Emotional Stress
- Allergies (endogenous or exogenous antigens)
- Physical stress
- Medications
- Geopathic Stress
- EMF/Enviropathic stress
- Inflammation
Examples of Medications that influence histamine levels
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (ibuprofen)
- Antidepressants (Cymbalta, Effexor, Prozac, Zoloft)
- Immune modulators (Humira, Enbrel, Plaquenil)
- Antiarrhythmics (propanolol, metaprolol, Cardizem, Norvasc)
- Aspirin – Histamine liberator
- Amitriptylene – DAO blocker
- Valium – DAO Blocker
- Lasiks – DAO Blocker
- Codeine – Histamine Liberator
- Augmentin – DAO Blocker
- Chloroquinine – DAO Blocker and Histamine liberator
- Quinine – Histamine liberator
- All X-ray contrast – Histamine liberator
- Metoprin – HNMT blocker
- Opiates (Heroin/Morphine…) – Histamine liberator
- Thiamine/Vit B1 – Histamine liberator
The effect of stress on histamine levels
- Histamine release increases during the periods of panic attack, especially when the adrenergic, “fight or flight” response is at its peak.• Histamine factors into the fight or flight because H3 histamine receptors in the brain promote the most “wakeful” firing pattern. In fact a sudden rush of histamine in the brain could contribute to a schizophrenic episode.
- Histamine is involved in panic events by causing a closing of the airways in the lungs. When released in the lungs, histamine causes the airways to swell shut in an attempt to close the door on offending allergens and keep them out. Panic attack periods are known for the sense of weight or contraction on the lungs.
Effects of Sleep on Histamine
- Sleep–It has been shown that histaminergic cells have the most “wakeful” firing pattern of any neuronal type. They fire rapidly during waking, and completely stop firing during sleep.
- The cell bodies of neurons which release histamine as a neurotransmitter are found in the posterior hypothalamus, in various tuberomammillary nuclei. From here, these histaminergic neurons project throughout the brain, to the cortex through the medial forebrain bundle.
- Antihistamines, substances that block the H1 histamine receptors improve sleep.
- Destruction of histamine releasing neurons, or inhibition of histamine synthesis leads to an inability to maintain vigilance.
- H3 receptor antagonists (which stimulate histamine release) increase wakefulness.
Influence of Histamine on Sex
- Histamine is released as part of sexual arousal from mast cells in the genitals, and histamine release has been connected to the sex flush in women.
- The female orgasm can be facilitated by supplemental folic acid along with niacin, which will increase histamine release.
- Men with high histamine levels may suffer from premature ejaculations.
Four types of histamine receptors in the body (H1, H2, H3, H4)
H1 Receptors
- Ileum contraction
- Modulate Circadian rhythms
- Itching
- Systemic vasodilation
- Broncho-constriction (allergy-induced asthma)
- pain and itching due to insect stings
- Are the primary receptors involved in allergic rhinitis symptoms and motion sickness.
- Initiates release of intracellular stores of Ca2+ and opens Voltage gated Calcium channels.
H2 Receptors
- Speed up sinus rhythms
- Stimulation of gastric acid (HCl) secretion
- Smooth muscle relaxation
- Inhibit antibody synthesis, T-cell proliferation and cytokine production.
H3 Receptors
- Decrease Acetylcholine, Serotonin and Norepinephrine neurotransmitter release in Central Nervous System (CNS).
- Presynaptic autoreceptors
H4 Receptors
- Found primarily in bone marrow and white blood cells. It is also expressed in the colon, liver, lung, small intestine, spleen, testes, thymus, tonsils, and trachea.
- Mediate mast cell chemotaxis. Histamine was shown to mediate signaling and chemotaxis of mast cells via the H4 receptor. This mechanism might be responsible for excessive mast cell accumulation in allergen sensitive tissues.
Problems with Antihistamines
- In HIT syndrome, the OTC and prescription antihistamines will cause of worsening of symptoms.
- Most over-the-counter antihistamines only block the H1 and/or H2 receptors.
- The excessive histamine is still circulating so it can be forced more to the H3 and H4 receptor pathways.
- H3 and H4 receptors are more related to Headaches, nausea, vomiting, vertigo, circadian rhythm problems, arousal, insomnia, appetite issues, memory problems, learning, and body temperature problems.
Methods to address Histamine Intolerance
- Eliminate foods high in Histamine (temporarily or long term).
- BRADE allergy desensitization with NeuroPhotonic Therapy (Available at the Biologix Center only).
- Eliminate medications that block DAO or HNMT, or that liberate histamine from the cells.
- Use BRS to identify remedy support the biochemical pathways to enable the body to produce DAO and/or HNMT.
- Restore probiotics, fecal microbiome transplants.
- Supplement diet with Diamine Oxidase (DAO), such as Hist-DAO (Xymogen).
- Treat Mental/Emotional (HPA axis) stress issues with BRS testing.
- Stabilize IgE mediated prostaglandin activation of mast cell release of histamine. (gamma linolenic Acid…Evening Primrose oil, Borage Oil, Black Currant Seed oil).
- Oxford University Peptide shots (Amino acid shots) to block the histamine receptors at the cellular level.
Oxford University Peptide Injections
- An antigen must first be attached to cell surface receptors on mast cells. This triggers a response that often includes the release of histamine. Most allergies involve the release of histamine and other pro-inflammatory substances.
- The Oxford Peptides (U.S. = Amino Acid Injections) physically block the receptors so that antigens cannot attach to the cell receptors, therefore no histamine is released by the mast cells.
Antihistamine Supplements
- Allermac (Jernigan)
- HistDAO (Xymogen)
- HistoCal (NutriWest)
- Resveratrol
- Turmero
- Whole System Histozyme (Nutriwest)
- Total CMO (NW) (autoimmune)
- Phoenix (Dr. Recommends)
- Isopathic Phenolics
- All homeo categories, Dairy, Beautox
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin E
- Sulfur (MSM)
- Essential fatty acids (GLA)
- Bromelain
- Boswellia (Frankincense)
- Pancreatic enzymes (Digest, Total Enzyme, Carbo-zyme, Amylase)
- R-lipoic acid
- Glucosamine hydrochloride
- Proanthocyanidins (Plant pigments)
- N-Acetyl Cystiene
- Allergic reactions typically have an adrenal component. Cortisol, is a strong anti-inflammatory agent. For this reason proper adrenal function plays an important role in mediating the histamine release and inflammatory reactions that produce the symptoms experienced with allergies.
- A vicious circle occurs with adrenal fatigue and the tendency to having allergies. The more histamine that is released the harder the adrenals have to work to produce more cortisol, thereby the more fatigued the adrenals become, which increases allergic reactions in a vicious circle.
Interactions of Nitric Oxide and Histamine
- Increasing Nitric oxide will down-regulate the release of histamine. (NO Saliva test strips; treat with Neo-40, NOx…)
- Histamine stimulates NO synthesis and release.
- Too much NO increases histamine as the body strives to bring down the high NO. (Be careful when treating low NO that new symptoms are not created by causing the over production of NO.)
- Several factors increase levels of NO in the body: Allergies (histamine), poor iron status, hypoxia (oxygen deficiency), estrogen dominance and Carbon Monoxide exposure.
Dietary Recommendations and Histamine
(While eliminating high-histamine foods from your diet is a great idea, diet alone is NOT a long term correction for the underlying HIT problems. You must work with your doctor to correct the enzymatic and histamine metabolic pathways.)
- Avoid or reduce eating canned foods and processed or ready made meals.
- Avoid or reduce eating ripened and fermented foods (older cheeses, alcoholic drinks, products containing yeast).
- Histamine levels in foods vary, depending on how ripe, matured or hygienic the foods.
- As much as it is possible, only buy and eat fresh products.
- Don’t allow foods to linger outside the refrigerator – especially meat products.
- Alcohol, primarily wine, champagne and beer
- Pickled or canned foods – sauerkraut. pickles, mayonnaise, olives
- Matured cheeses, including goat cheese
- Cured/Smoked meat products – salami, ham, sausages, bacon, salami, pepperoni, lunch meats and hot dogs
- Shellfish
- Various species of fish: mackerel, mahi-mahi, tuna, anchovies, sardines
- Beans and pulses – chickpeas, soy beans, peanuts
- Nuts – walnuts, cashew nuts, cashews, and peanuts
- Chocolates and other cocoa based products
- Avocados, eggplant, spinach, and tomatoes
- Most citric fruits, apricots, prunes, dates, figs, raisins
- Wheat based products
- Vinegar
- Processed and Ready-made meals
- Salty snacks, sweets with preservatives and artificial colorings
- Soured foods: sour cream, sour milk, buttermilk, sour dough bread
Foods that are Histamine Liberators
- Most citric fruits – kiwi, lemon, lime, pineapple, plums…
- Cocoa and chocolate
- Nuts
- Papaya
- Beans and pulses
- Tomatoes
- Wheat germ
- Additives – benzoate, sulphites, nitrites, glutamate, food dyes
Drinks that are Diamine Oxidase (DAO) Blockers
- Alcohol
- Black tea
- Energy drinks
- Green tea
- Mate tea
Antihistamine Herbs and Spices
- Amaranth seeds
- Anise
- Basil
- Berberine
- Carraway
- Chamomile
- Chili powder
- Cinnamon
- Clove
- Curry powder
- Echinacea
- wild oregano
- Fennel
- Fig
- Ginger
- Ginkgo
- Grapefruit
- Nutmeg
- Passionflower
- Tarragon
- Tumeric
- Skullcap
- Thyme
- Yarrow
- Papaya
- Reishi Mushroom
- Stinging nettle
Foods Low in Histamine
- Freshly cooked meat, poultry (frozen or fresh)
- Freshly caught fish
- Cooked eggs
- Gluten-free grains: rice, quinoa, corn, millet, amaranth
- Pure peanut butter
- Fresh fruits: mango, pear, watermelon, apple, kiwi, cantaloupe, grapes
- Fresh vegetables (except tomatoes, spinach, avocado, and eggplant)
- Dairy substitutes: coconut milk, rice milk, hemp milk, almond milk
- Cooking oils: olive oil, coconut oil
- Leafy herbs
- Herbal teas
Effects of Low Histamine (Histopenia)
- Histapenia (Low Histamine): It is found that 30-40 % of people with schizophrenia have low whole blood histamine levels and are over-methylated.
- People with low histamine tend to have more severe mental disorders and hallucinations, paranoid thoughts with less pronounced obsessions, despair, depression, low libido, anxiety, nervous legs and grandiosity.
- People with low histamine often have a multitude of food allergies and environmental allergies but they do not typically have seasonal allergies.
- Approximately 25% of bipolar patients have low histamine levels.
Biochemistry of Histopenia
- Low “Whole blood histamine”
- Low blood zinc
- Low basophils
- Elevated levels of serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine.
- Elevated copper, which is a brain stimulant and destroys histamine; causing brain dopamine levels to rise; copper then oxidizes catecholamines such as dopamine thus propagating neurotoxin formation. This causes paranoia and hallucinations in younger individuals, but depression may predominate in the older ones.
Testing for Histamine Intolerance (HIT): (Not all of these test must be performed to diagnose HIT.)
- Histamine Determination, Whole Blood
- Serum quantitative, Diamine Oxidase Activity Test
- Histamine 50-Prick Skin Test
- Serum Tryptase levels are persistently above 15 ng/mL
- 24-hour, Urine histamine metabolite, PGD2
- 11-β-prostaglandin F2 alpha